Podcast: Play in new window | Download
Updates:
- Update: Occupy The Justice Department
- Bradley Manning Trial Update: Attorney CCR Attorney Shane Kadidal
- Bradley Manning: A Show Trial of Secrecy by Michael Ratner
————
39 Ways To Limit Free Speech is the title Law Professor David Cole’s recent article. Earlier this month, a 29-year old citizen from Sudbury, Massachusetts named Tarek Mehanna was sentenced to seventeen and a half years in prison for translating a document. The text he translated from Arabic is “39 Ways to Serve and Participate in Jihad” and its all over the internet, you can read it says David Cole, but don’t try to translate it. One issue in the government’s prosecution of this case is the use of the decision from the Brandenburg v. Ohio case in which the Supreme Court established that standard in ruling that the First Amendment protected a Ku Klux Klansman who made a speech to a Klan gathering advocating “revengeance” against blacks and “Jews.”
- He was accused of providing material support to al-Qaeda by translating various documents and videos from Arabic into English. There’s no allegations that Mehanna ever met with or even talked to a member of al-Qaeda. There are no allegations that the translations were delivered to or provided to al-Qaeda which was the designated group.
- The government argued that because he translated these documents and put them up on the web and hoped to encourage people to support jihad and support al-Qaeda, that’s enough to constitute material support.
- Here’s an instant in which the government is prosecuting pure speech but no showing that the speech was connected to illegal conduct, no showing that it was intended to produce eminent lawless action, which the Supreme Court said is required to produce under Brandenburg.
- It’s enough that he put it up on the web and wanted to support al-Qaeda.
- If that’s a crime what about the New York Times when it does a report on one of the many messages Osama Bin Laden put after 9-11?
- I represented the Humanitarian Law Project in the case that went to the Supreme Court in 2010, in which the HLP was in engaging in advocacy of human rights and peace, clearly non-violent, non-criminal conduct.
- But because they wanted to do it to and with the Kurds in Turkey and particularly the political representatives of the Kurds in Turkey which is the Kurdistan Workers Party (designated as a terrorist organization) the government argued that it was a crime to teach the KWP to bring human rights claims in Geneva and work with them in peace overtures to the Turkish Government.
- The Supreme Court upheld that, but doesn’t apply to independent advocacy. (until now)
- Now if you wanted your speech to support terrorist organizations, even if you did it independently of that organization, even if you never met or talked to anyone in that organization, we can make it a crime.
- Very much about declaring a “new front” in the war on terror and the front is going after internet propaganda.
- To me it recalls the kind of aiding the enemy prosecutions we saw in World War 1.
- We as citizens need to be active in monitoring and pushing back against this material support statute.
Guest – Professor David Cole teaches constitutional law, national security, and criminal justice at Georgetown University Law Center. He is also a volunteer attorney for the Center for Constitutional Rights, the legal affairs correspondent for The Nation, a regular contributor to the New York Review of Books, and a commentator on National Public Radio’s All Things Considered. He has been published widely in law journals and the popular press, including the Yale Law Journal, California Law Review, Stanford Law Review, New York Times, Washington Post, Wall Street Journal, and Los Angeles Times.
——————-
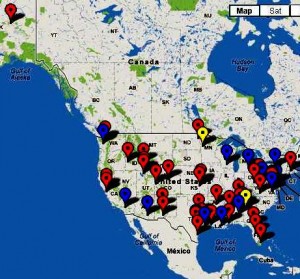
FAA Releases Lists of Drone Certificates—Many Questions Left Unanswered
Earlier this year we discussed the partnership with Cornell University and Technion-Israel Institute of Technology. The two institutions are working together to build a campus in New York City. Technion is involved with developing robotic weapons systems, which include aerial drones, and unmanned combat vehicle technology. There are many more universities involved with drone technology. Through a series of Freedom of Information requests by the Electronic Frontier Foundation, the FAA has been forced to reveal approximately 63 active drone sites. These sites are located in 20 states and their owners include military and universities. Universities include Cornell, (which we just mentioned) the University of Colorado, Georgia Tech, Eastern Gateway Community College and many more.
- We filed a FOIA request with the FAA last April asking for copies of all the certificates of authorization and the special air-worthiness certificates that the FAA issues to anybody to wants to fly a drone in the US.
- We asked for these lists which are called COAs, or Certificates of Authorization. The COAs apply to public entities like state and local law enforcement, universities, the federal government.
- We got two lists from the FAA and the FAA says these cover all of the entities that applied for an authorization to fly a drone in United States.
- They’re very interesting, the COA list includes some unsurprising entities like DARPA, DHS, Customs and Border Protection, the FBI, various branches of the military. We already knew those entities were flying drones.
- What was more surprising was the number of universities and colleges on the list.
- Universities that have an aerospace engineering program they may be seeking authorization so the students can learn about and design drones.
- The Electronic Frontier Foundation is a civil liberties non-profit, we focus on civil liberties and new technology, and we’re concerned about surveillance equipment used by the government.
- Drones are a duel use technology, they can be used for good or for bad.
- They can see inside buildings, survey an area at night with heat sensors, they also have the ability to carry communications intercept tools. You could swap out various payloads on a drone.
- Then of course these drones can carry weapons.
- You can build your own drone, DIYDrones.
- We don’t know too much about what’s going on now. The reason the EFF file the FOIA request in the first place is that we just don’t know how agencies are using these drones.
- What we found is that a lot of the police forces that have drones are required to fly them under 600 feet. If its something that flying under 600 feet you’re going to be able to see that.
- Congress was getting a lot of pressure, and the FAA was getting a lot of pressure from state and local law enforcement, the military and the federal government to authorize more drones to be used in the United States.
- We’ve heard from the Congressional Research Service that 1 in 3 warplanes right now is a drone.
- The wars are going to end and the military is going to want to something with these drones.
Guest – Jennifer Lynch, staff attorney with the Electronic Frontier Foundation and works on open government, transparency and privacy issues as part of EFF’s FOIA Litigation for Accountable Government (FLAG) Project. In addition to government transparency, Jennifer has written and spoken frequently on government surveillance programs, intelligence community misconduct, and biometrics collection. Prior to joining EFF, Jennifer was the Clinical Teaching Fellow with the Samuelson Law, Technology & Public Policy Clinic at UC Berkeley School of Law. At the Samuelson Clinic, Jennifer specialized in privacy and intellectual property issues, including investigations on social media, privacy and the smart electrical grid, digital books, and open source regimes for biotech. Before the Clinic, Jennifer practiced with Bingham McCutchen in San Francisco and clerked for Judge A. Howard Matz in the Central District of California. She earned both her undergraduate and law degrees from UC Berkeley.
—————————–