Academic Freedom, Censorship, Civil Liberties, Civil Rights, Freedom Of Speech, Human Rights, Immigration
Podcast: Play in new window | Download


Federal Funding Capitulation: Northwestern Joins Columbia and Brown University
The day after Thanksgiving last year, in an deserved win for Donald Trump and a sad loss for higher education, Northwestern University joined Columbia and Brown universities by capitulating to Trump’s yearlong campaign to bribe American colleges and universities into paying ransom to restore millions of dollars of federal research grants he had illegally suspended on the pretext that the universities had failed to adequately monitor antisemitism on their campuses. Northwestern agreed to pay the Trump administration $75 million and entered into a three-year settlement agreement containing a host of provisions seriously impairing Northwestern’s educational independence and academic freedom.
Within days of the settlement, two law professors from Northwestern’s own law school, Heidi Kitrosser and Paul Gowder, went public alleging that the agreement was illegal and unconstitutional. They wrote: “Our analysis lays bare that the government’s extortion of Northwestern –unlawfully freezing funds to force the university to make a ‘deal’ – has nothing to do with actual legal violations at Northwestern (which, if they existed, could and should have been addressed through established legal channels), and everything to do with a campaign to encroach on the autonomy of Northwestern and other institutions of higher education, and to impose on them the Trump Administration’s reactionary political agenda.”
Guest – Heidi Kitrosser is the William W. Gurley Professor of Law at Northwestern Pritzker School of Law. She is an expert on the constitutional law, government secrecy and free speech law. Her book, Reclaiming Accountability: Transparency, Executive Power, and the U.S. Constitution, was awarded the 2014 IIT Chicago-Kent College of Law / Roy C. Palmer Civil Liberties Prize. She is a 2017 recipient of a Guggenheim Fellowship. Prof Kitrosser has been involved in drafting several amicus briefs in recent years challenging threats to free speech, academic freedom, and government accountability. She is also a founding steering committee member of the Free Expression Legal Network. FELN is a network of law school clinics, academics, and practitioners (including nonprofits) across the country that seeks to promote and protect free speech, free press, and the flow of information.
—-


Prairieland Case Labeled First Prosecution of Antifa
On July 4, a small group of people gathered in front of the Prairieland Detention Center in Alvarado, Texas. They were protesting in solidarity with immigrants and ICE detainees, using noise and fireworks—ordinary tools on Independence Day. Police later claimed that an Alvarado officer was involved in an exchange of gunfire after arriving near the protest, sustaining minor injuries. Six months later, authorities have still not produced hospital records substantiating those claims.
Despite that, a federal grand jury in Fort Worth indicted nine people in connection with the July protest/ Seven others were charged separately. Charges include rioting, use of weapons and explosives, obstruction, providing material support to terrorists, and attempted murder of an Alvarado police officer and unarmed correctional officers.
The Trump administration has publicly framed the Prairieland case as the first prosecution of “Antifa.” On September 25, the White House issued a directive ordering federal law enforcement to prioritize so-called Antifa-linked activity as domestic terrorism. Kash Patel has echoed that framing, publicly labeling the defendants “Antifa-aligned anarchist violent extremists.”
Guest – Dario Sanchez, one of the defendants. A computer science teacher, Dario is caretaking for his injured partner since 2024. He was arrested at a pre-dawn raid on their home with no resistance. https://prairielanddefendants.com/

—————————-
Censorship, Civil Liberties, Criminalizing Dissent, Economics, Freedom Of Speech, Gaza, genocide, Human Rights, U.S. Militarism, Violations of U.S. and International Law
Podcast: Play in new window | Download


From The Flag To The Cross: Fascism American Style
From The Flag To The Cross: Fascism American Style is the title of a recently published anthology edited by Zachary Sklar and our own Michael Smith. Co-host Jim Lafferty wrote the introduction. The book draws from seven key interviews with prominent socialist thinkers in the United States and Canada. They include Margaret Kimberly, Henry Giroux, Dianne Feeley and Bill Mullen. Bill will also be joining Michael and Jim in the guest seat. He’s Professor Emeritus of American Studies at Purdue University and author of We Charge Genocide! American Fascism and the Rule of Law.
Chris Hedges who is also included in this book, writes “when fascism comes to America, it will be mass of recitations of the pledge of allegiance, the Christian cross and the flag.” We’ll explore these frayed boundaries of Christian fascism, capitalism, and the assaults on free speech and censorship while highlighting the strategies of community based actions.
Guest – Michael Steven Smith is the author, editor, and co-editor of many books, mostly recently Imagine: Living In A Socialist U.S.A. and “The Emerging Police State,” by William M. Kunstler. He has testified before committees of the United States Congress and the United Nations on human rights issues. Mr. Smith lives and had practiced law in New York City with his wife Debby, where on behalf of seriously injured persons he sues insurance companies and occasionally the New York City Police Department.
Guest – Jim Lafferty is the Executive Director Emeritus of the National Lawyers Guild in Los Angeles and the host of The Lawyers Guild Show on Pacifica Radio’s Los Angeles station, KPFK. Jim has been a national leader in the peace and social justice movement for 60-years. He served as a national Coordinator of the National Peace Action Coalition, the group that organized the largest protests against the U.S. war in Vietnam, and in leadership positions in other peace coalitions opposing various imperialist U.S. wars. In the early 1960’s he was the national Director of the National Lawyers Guild during its historic work in the South. In the mid-1960’s until the 1980’s, Jim was in the private practice of law in Detroit, Michigan, where he specialized in Selective Service law, employment discrimination law, and civil rights law. He serves on the governing board of the A.C.L.U. of Southern California, is a member of the steering committee of the national Julian Assange Defense Committee, and a Fellow at the Institute for the Humanities at the University of Southern California.
Guest – Bill Mullen is professor emeritus of American studies at Purdue University and the co-founder of The Campus Anti-fascist Network. He’s also co-author of The Black Antifascist Tradition and We Charge Genocide: American Ashes and the Rule of Law. He’s a contributor to the just published Law And Disorder book From the Flag to the Cross: Fascism American Style.

——————————————-
Academic Freedom, Censorship, Civil Liberties, Economics
Podcast: Play in new window | Download
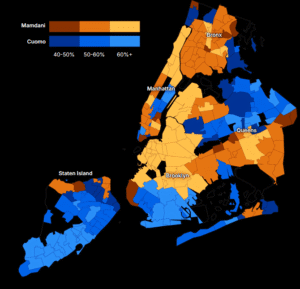

Socialist Democrat Voted Into NYC Mayoral Seat: What Happens Now?
Thirty-three year-old Zohran Mamdani, an immigrant from Uganda, a Muslim, and a member of the Democratic Socialist of American won an overwhelming victory in New York City’s primary in September’s and then won the mayoral race in New York City December 4. His team of some 100,000 door knockers and canvassers swept the charismatic Mamdani into first place over the former governor and main line Democrat Andrew Cuomo. Cuomo was supported financially and politically by 28 different billionaires, Wall Street, and the real estate interests. The top of the Democratic party refused to endorse Zohran even after he won the Democratic primary and recently Trump smeared Zohran as a “lunatic communist“ and has already cut off $18 billion of federal funding for the state of New York.
The victory of Mamdani and the magnificent movement behind him came after the No Kings demonstrations attended by millions across the country. It is the most significant development so far in the fight back against the oligarchs, authoritarians and fascists forces in the United States. The Mamdani success has changed the relationship of forces somewhat between the American people and their rulers like nothing we have seen since a huge rebellion against the Vietnam war in 1968. What are its implications for New York City and beyond, the growth and influence of socialist ideas and for the DSA?
Guest – Historian Paul LeBlanc, professor emeritus of history at LaRoche University in Pittsburgh and an active member of the Pittsburgh chapter of the DSA. He is the author of many books on socialism and labor history and most recently a contributor to A User’s Guide to the DSA with an article titled A Effective Force for Socialism.–
—-


Lawsuit Charges That California Law Illegally Muzzles Students and Teachers on Palestine
Beginning January 1, 2026, teachers in California classrooms will have to look over their shoulders to avoid running afoul of an alarming new “antisemitism” law. On October 7, despite widespread opposition from teachers’ unions, civil rights groups, and education advocates, Gov. Gavin Newsom signed AB 715. It amends the California Education Code to police what teachers can teach and what students can learn about Israel and Palestine.
Under this law, teachers could be charged with unlawful discrimination and disciplined “if they expose their students to ideas, information, and instructional materials that may be considered critical of the State of Israel and the philosophy of Zionism,” according to a lawsuit filed on November 2 by the American-Arab Anti-Discrimination Committee (ADC).
Guest – Marjorie Cohn is Professor Emerita at Thomas Jefferson School of Law, Dean of the People’s Academy of International Law, and former president of the National Lawyers Guild. She is a legal and political analyst who does media commentary and writes columns on Truthout and other outlets, and she a former host on Law and Disorder radio. Her most recent book is Drones and Targeted Killing: Legal, Moral, and Geopolitical Issues. Marjorie wrote an article that was published earlier this month on Truthout, titled Lawsuit Charges That California Law Illegally Muzzles Students and Teachers on Palestine.

———————–
Academic Freedom, Censorship, Civil Liberties, Freedom Of Speech, Right To Dissent
Podcast: Play in new window | Download


The Library Freedom Project
Soon after the attacks of September 11, 2001, when federal agents demanded library circulation records under the USA Patriot Act, librarians became unlikely whistleblowers for democracy. The “Connecticut Four” successfully sued the FBI in 2005 over secret National Security Letters that sought patron data and imposed gag orders. They reminded the nation that a book borrowed in silence should never be grounds for suspicion.
The Library Freedom Project was born in this climate of intrusion. It equips librarians with new skills: teaching prompt literacy so they can critically evaluate generative AI outputs; training them in deepfake and voice-clone detection; and raising awareness about the growing use of AI surveillance in schools and communities. In doing so, the project prepares librarians to guide the public through one of the most disruptive technologies of our time.
Guest – Alison Macrina, activist librarian and founder of the Project. Since 2015, she has built a network of librarians committed to protecting privacy, defending intellectual freedom, and challenging power structures through organizing and education. Recognized with a 2023 Electronic Frontier Foundation Award, Macrina and her colleagues argue that libraries are among the last truly public goods—accessible to everyone, regardless of income or background—and that defending these spaces means defending the very foundation of free expression and information democracy.
—-


Media Censorship: A Structural Problem
As the Trump administration seeks to expand presidential authority, it’s not surprising that the First Amendment is making headlines. Enacted in 1791 to protect fundamental freedoms – such as speech and the press – it serves as a safeguard against potential abuses of government power, including censorship and other efforts to stifle dissent. Trump and his allies have made no secret about their intention to silence prominent comedians who are critical of the administration.
On July 17th, CBS announced the cancellation of The Late Show with Stephen Colbert, a move that Trump publicly applauded, adding that Jimmy Kimmel would be next. Within days, the FCC approved a merger involving CBS’s parent company, Paramount. On Sept. 17th, FCC Chair Brendan Carr warned that if Disney did not suspend Jimmy Kimmel for making comments about MAGA and Charlie Kirk, the FCC could get involved with ABC’s licensing. Disney immediately took Jimmy Kimmel Live off the air. And even though it started back up on Sept. 23rd, many ABC affiliates refuse to air it. Oh, and by the way, Trump has warned that Jimmy Fallon and Seth Meyers at NBC will be next to go.
Guest – Jeff Cohen is a highly regarded progressive critic of the media. Indeed, he was recently quoted in an important article in the Washington Post about the disclosure that FOX News hosts were advising the White House during the January 6th insurrection. Jeff Cohen, along with Martin Lee, were the co-founders of Fairness and Accuracy in Reporting, or “F.A.I.R.,” which is the anti-corporate media group that monitors and reports on the mainstream media’s bias, spin and misinformation. Jeff Cohen is also a lecturer on these matters and the author of the book, Cable News Confidential.

————————-
Censorship, Civil Liberties, Civil Rights, Freedom Of Speech, Human Rights, Supreme Court
Podcast: Play in new window | Download


The First Amendment Heavily Tested Under Trump Administration
The First Amendment is being tested in many arenas not only in response to various Executive Orders which Donald Trump has issued in his second term, but also in state legislatures which are experimenting with how far the government can go in restricting freedom of speech.
In Free Speech Coalition v. Paxton, the US Supreme Court upheld a Texas law requiring age verification for access to Internet porn sites. In 2024, Mississippi enacted House Bill 1126 after a Mississippi teen became the victim of sextortion on Instagram and died by suicide. That law requires young people to obtain their parents’ consent before they can create social-media accounts. On August 13, the US Supreme Court issued a brief unsigned order allowing that law to go forward despite a lower court injunction.
Meanwhile, South Park is savagely ridiculing Donald Trump, CBS capitulated when Trump sued them over a 60 Minutes segment, and a conservative federal appeals court struck down an injunction for an on-campus drag show. There’s a lot going on when it comes to free speech.
Guest – Robert Corn Revere has been a First Amendment litigator for more than four decades. He is Chief Counsel for the Foundation for Individual Rights and Expression or FIRE. He is the author of The Mind of the Censor and the Eye of the Beholder: The First Amendment and the Censor’s Dilemma, which explores how free expression became a part of America’s identity. FIRE filed an amicus brief in support of Net Choice in one of the cases we’re discussing today.
—-

Chambers v. Florida and the Criminal Justice Revolution
In 1933, four young Black farm workers in Pompano, Florida, were arrested for the murder of a white shopkeeper. With no lawyers and no meaningful due process, for a week they were held, beaten, threatened with lynching, and ultimately forced to sign confessions. Their convictions and death sentences seemed almost certain in the Jim Crow South. But 7 years later, the U.S. Supreme Court reversed those verdicts in a unanimous ruling, declaring that confessions obtained under psychological coercion rendered them involuntary and violated the 14th Amendment.
In Chambers v. Florida and the Criminal Justice Revolution, author Richard Brust vividly revisits this often-overlooked case. Chambers opened the door to the Warren Court’s criminal procedure revolution, laying the foundation for decisions such as Miranda v. Arizona. The book also highlights the lawyers and communities behind the case. Jacksonville attorney Simuel McGill, one of Florida’s few Black lawyers, kept the appeals alive until the case reached Washington.
Guest – Richard Brust is a journalist and historian whose work focuses on law, politics, and American history. He was a longtime editor for the American Bar Association’s ABA Journal and has written extensively about the courts and the evolution of U.S. legal culture.

——————————-
Academic Freedom, Censorship, Civil Liberties, Civil Rights, Criminalizing Dissent, Freedom Of Speech, Supreme Court
Podcast: Play in new window | Download


Stephen Rohde: Checks, Balances And Separation Of Powers
This half-hour, we continue our ongoing effort to understand in real time, the upheavals taking place within our US government, as well as the blitz of attacks on the rule of law – and that includes attacks on judges, lawyers, academics, students, and virtually anyone else who is critical of the Trump Administration’s policies and actions.
Today, we’ll be particularly focused on recent Supreme Court decisions that have paved the way for Trump to dismantle the Department of Education and numerous government agencies. The decisions also Limit the public’s ability to challenge government overreach and have led to swift deportations to countries in which detainees have no prior connection. We’ll also follow-up on the critically important case on First Amendment and academic freedom, American Association of University Professors v, Rubio, which is in trial right now in Boston.
Guest – Stephen Rohde is a legal scholar, writer, lecturer and political activist, who practiced civil rights and civil liberties law for over 50 years. He’s past chair of the ACLU Foundation of Southern California and past national chair of Bend the Arc, a Jewish Partnership for Justice. He’s also a co-founder and chair of Interfaith Communities United for Justice and Peace, and a Special Advisor on Free Speech and the First Amendment for the Muslim Public Affairs Council. He hosts the podcast, Speaking Freely.
—-


The MAGA Ideology and the Trump Regime
As V.I. Lenin observed, “There are times in history when nothing happens for decades and other times when decades happen within days” He should know. He was the leader of the Russian revolution which overthrew the feudal Tsar and changed the history of the 20th century. We are living in a time when history is unfolding very rapidly. Trump and his coterie of the upper 1/10 of 1 percent aligned with the mostly lower middle class MAGA movement have taken huge steps upending and overturning the kind of democracy, however, limited by race and class, that we have lived with since gaining independence from England 250 years ago.
We are experiencing the transition to a new absolutist executive. Trump and the ideologues who have shaped his MAGA movement is a president who acts on the premise that whatever he does is lawful. He claimed full power to close down departments like the Department of Education, impound congressionally authorized spending, deport people without due process, while ignoring the courts. This is what he calls “a unitary executive.”
The classic definition of fascism is that it is one of the political forms that capitalism may assume in its monopoly imperial phase. It has a material foundation in a tenuous alliance between sectors of the extremely rich monopoly capitalists and a mobilized lower middle class. The key to fascist rule is the privatization of large parts of the government on behalf of the monopoly class. This ideology now in ensconced in the White House.
The right wing is opposed to environmental governance, they don’t believe in climate change. They are against open borders, universal healthcare and green energy. Those who advocate for these beneficial movements are called “cultural Marxists.” They refer in a derogatory way to all contemporary progressive political causes. They call it woke. They use the term as it means to belittle all social justice struggles against racism and inequality, Its most common usage is as a racist dog whistle.
These fascists want to secure their rule by getting control of the entire cultural apparatus of society, a process that the Nazis, the German fascists of their time,called “bringing it into line.” The current attack on universities is the most recent example.
Guest – John Bellamy Foster is professor emeritus of sociology at the University of Oregon. He is a prominent scholar on ecology and the author of many books, including Trump in the White House: Tragedy and Farce. Professor Foster is the editor of the venerable socialist magazine “Monthly Review“ and the author of the article The MAGA Ideology and the Trump Regime in its recent May 2025 issue.

——————-






















